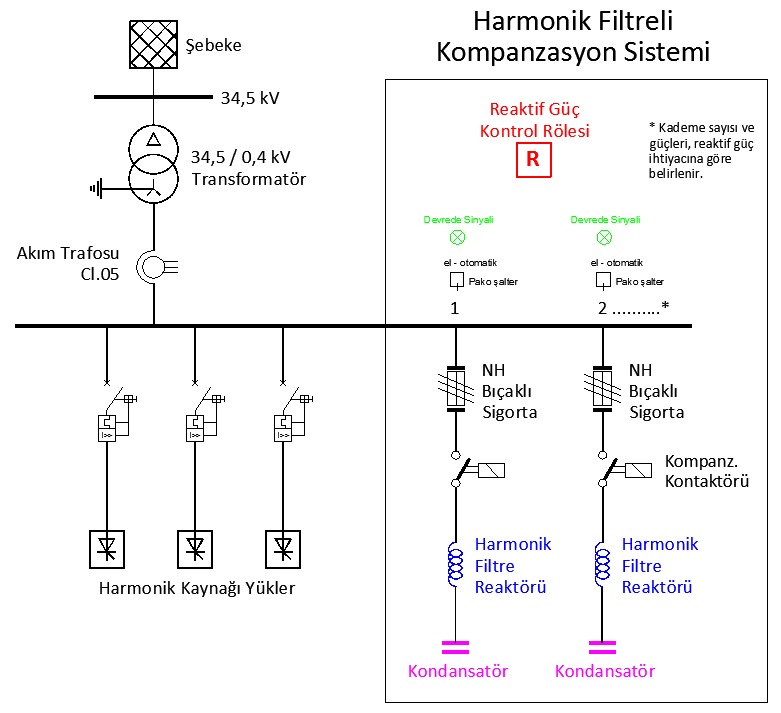
Does Your Business Comply with Harmonic Limit Values?
The “SERVICE QUALITY REGULATION REGARDING ELECTRICITY DISTRIBUTION AND RETAIL SALES” published in the Official Gazette dated 21 December 2012 and numbered 28504 sets the definitions and rules regarding energy quality. According to this regulation, distribution companies are obliged to provide their subscribers with the voltage quality conditions specified in the TS EN 50160 Standard. On the other hand, subscribers are obliged to comply with the current harmonic limit values specified in the IEEE 519 Standard (Table 11). According to Article 23 – Clause three, it is stated that if the user, who causes harmonic distortion in the network, does not comply with the limit values until the end of the given time, he will be disconnected. You can download the relevant regulation from the link below.
https://www.epdk.gov.tr/Detay/DownloadDocument?id=y/bTg3OJP/s=
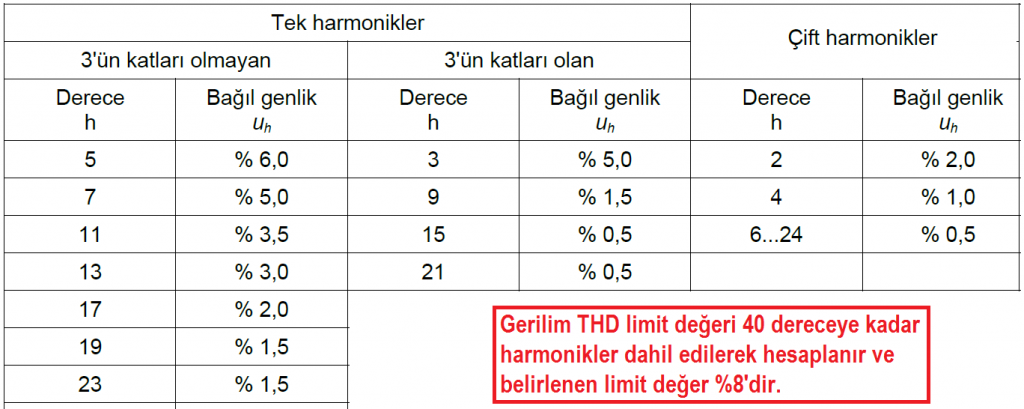
TABLE-11 LIMIT VALUES ACCORDING TO MAXIMUM LOAD CURRENT (IL) FOR CURRENT HARMONICS
| Isc / IL | 3-5 7-9 | 11-13-15 | 17-19-21 | 23-25-27 29-31-33 | 35 ve üzeri | TTB (TDD) |
| < 20 | 4 | 2 | 1,5 | 0,6 | 0,3 | 5 |
| 20 < 50 | 7 | 3,5 | 2,5 | 1 | 0,5 | 8 |
| 50 < 100 | 10 | 4,5 | 4 | 1,5 | 0,7 | 12 |
| 100 < 1000 | 12 | 5,5 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 15 |
| > 1000 | 15 | 7 | 6 | 2,5 | 1,4 | 20 |
Even harmonics are limited to 25% of the value defined for the next odd harmonic.
What do the values in the table represent?
The values in the table represent the limits of the current harmonics drawn by the enterprise from the network. In order to determine which limit values are, first of all, the ISC / IL value must be calculated. The ISC value is the short-circuit current at the network connection point of the enterprise (this value can be calculated by the relevant distribution company), and the IL value is the basic component value of the maximum load current drawn from the network for 1 year. It is not always possible to determine these values precisely. In such cases, approximate values are used. The values in the first line represent the order of the harmonic component, and the values in the other lines represent the percentage ratios of the measured harmonic currents to the IL value.
What is TTB (TDD)?
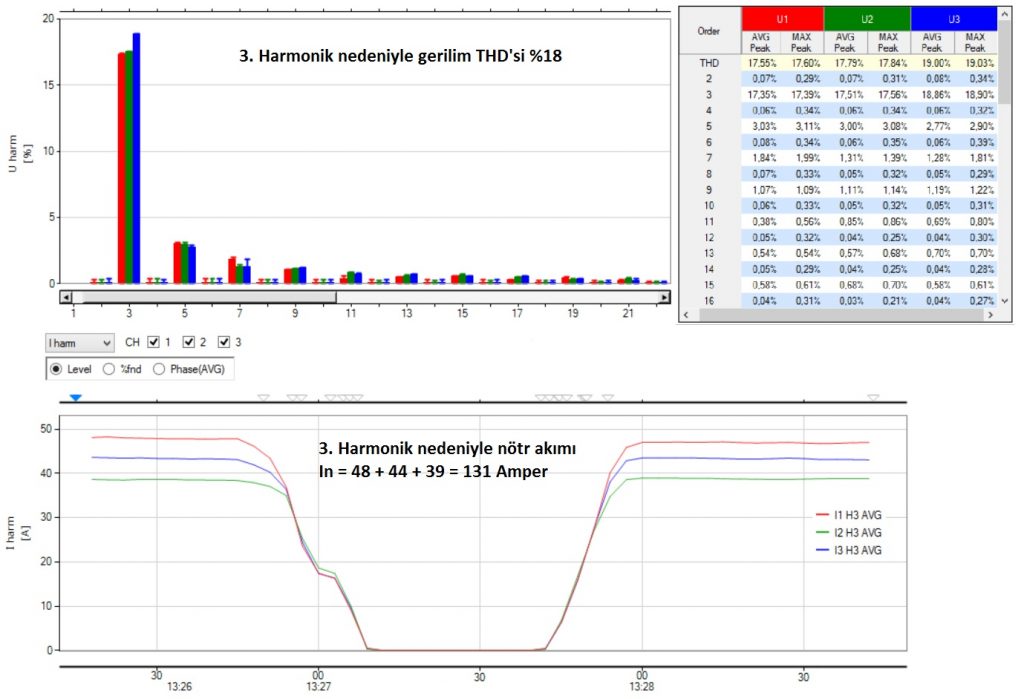
The term TTB (Total Demand Distortion in English) is often confused with the term THD. TTB represents the ratio of the vector sum of the harmonic distortions in the current to the IL value.
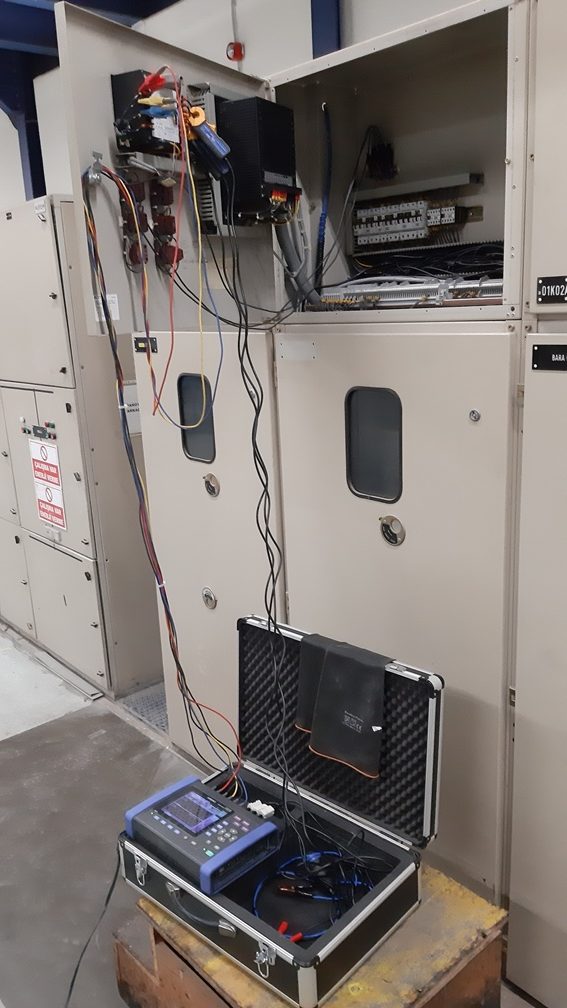
HOW LONG SHOULD THE HARMONIC MEASUREMENT TIME BE?
The harmonic measurement period is defined as “one-week uninterrupted measurement time defined in TS EN 61000-4-30” in the relevant regulation.
WHERE SHOULD THE HARMONIC MEASUREMENT BE PLACED?
The harmonic measurement location must be the mains connection point of the facility. This point is usually the point where the meter is the basis for billing. If there is a transformer between the mains connection point and the measurement point, the measurements taken from the low voltage main switch of the facility should be reduced to the mains connection point.
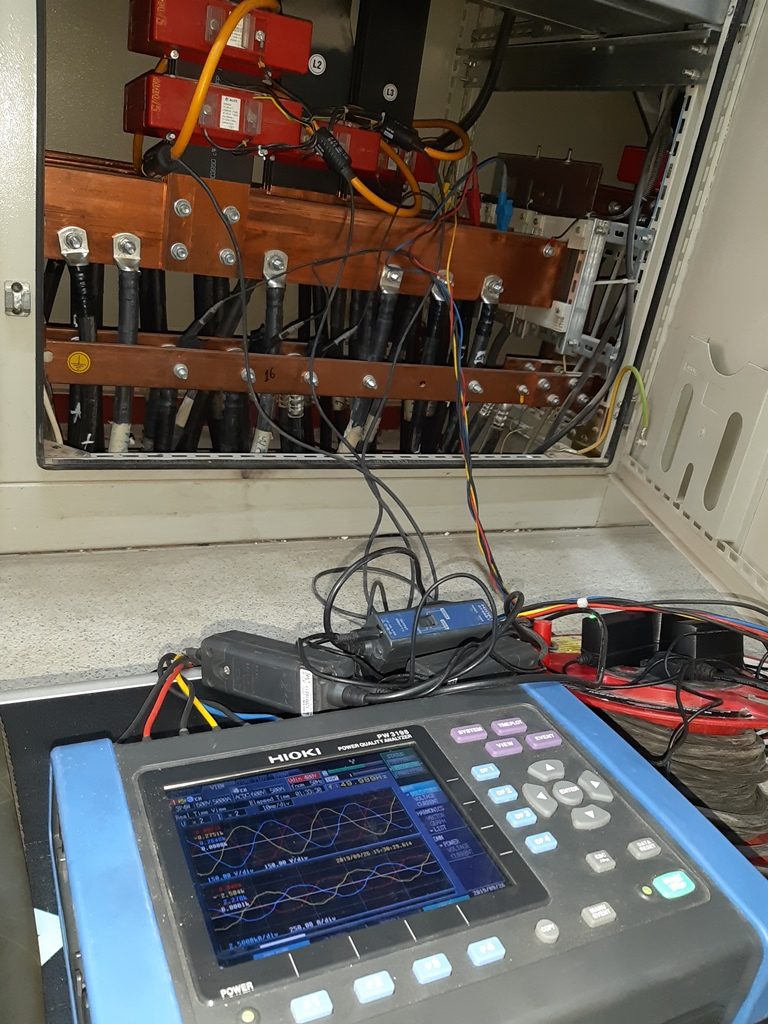
WHAT ARE THE FEATURES SHOULD A HARMONIC MEASUREMENT DEVICE HAVE?
The characteristics that the harmonic measuring device must have are determined in the IEC 61000-4-30 standard. According to the relevant standard, the device to be used in harmonic measurement must measure in Class A properties.
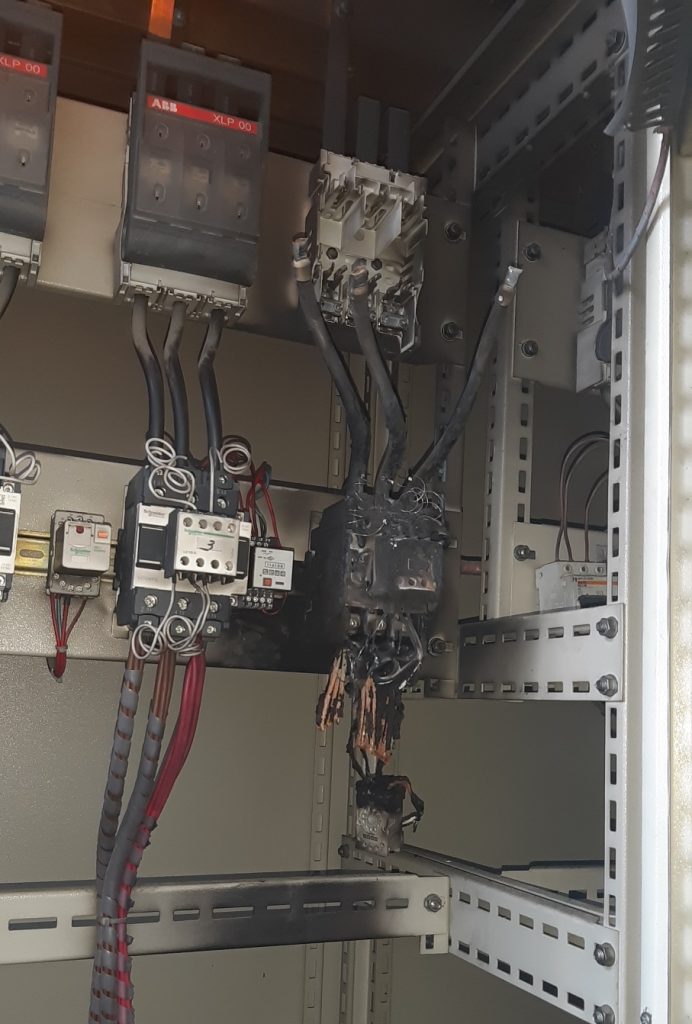
As a result of the measurements, it is checked whether the harmonic values of the facility exceed the limit values. If it is determined that the limit values are exceeded, the source causing this should be determined and the most appropriate solution should be designed.
HAVE HARMONIC MEASUREMENT AND ANALYSIS DONE IN YOUR FACILITY. COMPLY WITH HARMONIC LEGISLATION. USE MORE RELIABLE AND MORE EFFICIENT ENERGY.